Every major broadcaster acknowledges that it has to consider disaster recovery. Apart from meeting audience expectations, if a channel is off air, it cannot transmit commercials. Without commercials, it has no income. Getting the station back on air is clearly vital, says Michael Rebel.
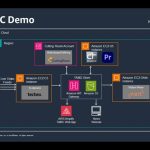
In today’s world, with reliable technology available, a large investment in replicating the primary playout centre could be seen as wasted money: a lot of hardware (and real estate) that will never go to air. How then do we ensure business continuity through a disaster recovery site that gets the channel on air in the shortest possible time, can be operated from anywhere and involves the least amount of engineering support? The answer that broadcasters are increasingly turning to is the cloud.
Start-up costs aside, it can be extremely cost-effective to keep a standby system in the cloud, ready to start when you need it, dormant when you do not. For many, cloud-based disaster recovery serves as a good, practical first experience of media in the cloud.
Whichever provider you choose, what you buy from them is access to effectively infinite amounts of processing power and storage space. We have worked extensively with AWS and other cloud suppliers, but AWS also offers some media-specific services (through its acquisition of Elemental) like media processing, transcoding and live streaming.
It is important to bear in mind that moving to the cloud is not an all-or-nothing, irreversible decision. The very nature of the cloud means it is simple to flex the amount of processing you put there, so if you decide to back away, it’s simple to do so.
The cloud is an element within the IP transition. You decide when and how to make that transition, and when and how much to use the cloud. For many broadcasters, disaster recovery is an excellent way to try out cloud services.
Keeping it familiar
With today’s software-defined architectures, systems should perform identically whether they are in dedicated computers in the machine room, virtualised in the corporate data centre, or in the cloud. Consistent operation is especially important in disaster recovery deployments. If disaster strikes, the last thing you want is operators scrabbling around trying to make sense of an unfamiliar system.
That does not mean the primary system and the disaster recovery site must be identical. But with a well-designed cloud solution, you should be able to emulate the same user interfaces. This makes it easy for the operators to switch back and forth between the two different environments.
It also means you can set resilience and availability by channel. You might want your premium channels to switch over to disaster recovery in seconds, for example, while some of your secondary channels can be left for a while. That is a business decision.

Content is still king
One of the common misconceptions about cloud playout is that synchronising content between premises and the cloud demands a lot of bandwidth and potentially high costs. This need not be the case.
Faced with the imminent obsolescence of video tape libraries, and wary of the eternal cost of maintaining an LTO data tape library, many broadcasters are looking to archive in the cloud. You load the content once, confident that all the technology migration and maintenance will be carried out flawlessly by someone else.
You may have collaborative postproduction by hosting content and decision lists in the cloud. Content – programmes and commercials – can be delivered direct to the cloud. Playout, archiving, post and traffic may be managed as separate departments, but if you combine them, content is only delivered to the cloud once. It is then available for playout without the high egress costs, and is securely stored at significant cost savings.
“Disaster recovery is fundamentally a business issue, a strategic decision. Using the cloud can deliver the best total cost of ownership, but it can also be a valuable stepping stone in a broadcaster’s transition to IP connectivity and outsourced hosting” – Michael Rebel, Director of Solution Architecture, Imagine Communications
Outsourcing security
Broadcasters have traditionally sought very high availability from the technology delivering premium channels. ‘Five nines’ used to be regarded as the gold standard – 99.999% up time. Even that, though, is equivalent to about 5 ¼ minutes of dead air a year.
AWS offers its broadcast clients unimagined availability, up to maybe nine nines – effectively zero downtime. And it achieves that without any maintenance effort on your part: no disk replacement, no routine cleaning of air conditioning, no continual updates of operating systems and virus protection. If the disaster is that your building has to be evacuated because of detected cases of a communicable disease, playout operators can work from home with exactly the same user interface and functionality as if they were sitting in the MCR.
If you want hot standby (complete parallel running in the cloud for almost instantaneous failover), then the technology allows it, if you choose to pay for the processing time.
Alternatively, pick your own level of cold or warm standby, confident that even from cold, loading and booting the channel playout instances can be accomplished in just a couple of minutes.
Cyberattacks are becoming an all-too familiar headline. Other industries have seen crippling incursions and software systems held to ransom. Developing a business continuity strategy that protects from such attacks is paramount.
Again, the cloud is the right solution. A good cloud provider delivers better data security than you can. AWS has thousands of staff with the word ‘security’ on their business cards. While no organisation can be perfect, a good cloud provider gives you your best shot at complete protection, because that is its business. The alternative is to build your own data security team: an unnecessary overhead and a challenge to develop, recruit and manage.
AWS is even used by the US intelligence community, which suggests that it is probably working.
“It is important to bear in mind that moving to the cloud is not an all-or-nothing, irreversible decision. The very nature of the cloud means it is simple to flex the amount of processing you put there, so if you decide to back away, it’s simple to do so” – Michael Rebel, Director of Solution Architecture, Imagine Communications
Doing it live
One comment often heard is that you cannot run live channels or live content from the cloud. This is not true. You can implement primary playout systems that feature live content.
The biggest requirement for sports television, however, is that live should be absolutely live: no one wants to hear their neighbours cheer and wait to find out why. Minimum latency is also critical for the big money business of sports books.
As consumer preferences move from broadcast to streaming, what happens after the master control switcher becomes ever more complicated in preparing the output for all the different platforms? That level of signal processing is better done in the cloud, especially with transcoding-as-a-service providing high-performance, affordable delivery.
Stepping stone to next-gen playout
Disaster recovery is fundamentally a business issue, a strategic decision. Using the cloud can deliver the best total cost of ownership, but it can also be a valuable stepping stone in a broadcaster’s transition to IP connectivity and outsourced hosting. The technical and operational teams gain experience and confidence in the cloud as a suitable broadcast platform. Routine rehearsals of business continuity mean operators learn how similar the performance of the cloud and on-premises systems are, and how the user interface seamlessly switches from one to the other.
This experience gives confidence to move on towards a completely cloud future. Pop-up channels can be created in minutes not months, so it is easy to service sports events or music festivals, while only paying for processor time when you need it. The cloud is infinitely scalable, so you can add channels or services, support new delivery platforms, and test market 4K and HDR.
The direct link between the cost of delivery and the revenue won makes for easier business management.
As the legacy playout network reaches life expiration, broadcasters know what the cloud can do and have built up solid information on the costs of operating in the cloud. That knowledge will be invaluable in evaluating proposals for the next generation of playout.