AI, ML and cloud are key technology drivers for closed captioning, subtitling and audio dubbing captioning, says Manik Gupta.
Over the last few years, consumption of video streaming services has risen exponentially – especially for subscription video-on-demand (SVOD), which has skyrocketed. Research shows that global SVOD subscriptions are expected to increase by 491m between 2021 and 2026, reaching 1.64bn. This is a huge leap forward in terms of subscriber numbers. Increasingly, SVOD services such as Netflix and Amazon Prime Video are relying on international subscribers to drive subscriber growth. Netflix is now available in more than 190 countries.
As video service providers look to globalise their content, closed captioning, subtitling and audio dubbing are becoming even more crucial for SVOD services. Through captions and subtitles, service providers have been able to broaden their reach and make streaming content accessible to millions of viewers across the globe with ease. Audio dubbing is equally critical in creating content for different geographies and reaching new, untapped audiences, because it allows video service providers to add language-specific content to the original audio.
However, preparing content in various languages can be a bit of a challenge. Roughly 6,500 different languages are spoken around the world, each with its own distinct differences, which poses a problem for closed captioning, subtitling and audio dubbing. As video service providers work toward streamlining delivery, it is becoming increasingly imperative to examine the latest technology trends to offer exceptional streaming quality and further expand their footprint.
AI/ML- and cloud-based solutions simplify delivery
Historically, captioning and subtitling have been manual-intensive processes. However, the tide is turning toward a more automated solution to meet captioning and subtitling needs. Now that OTT service providers are managing a massive amount of streamed content for a global audience, they require more efficient workflows. The cost and time involved with having to caption and subtitle everything manually has become too big of a burden. On average, captioning costs $5-10 per minute.
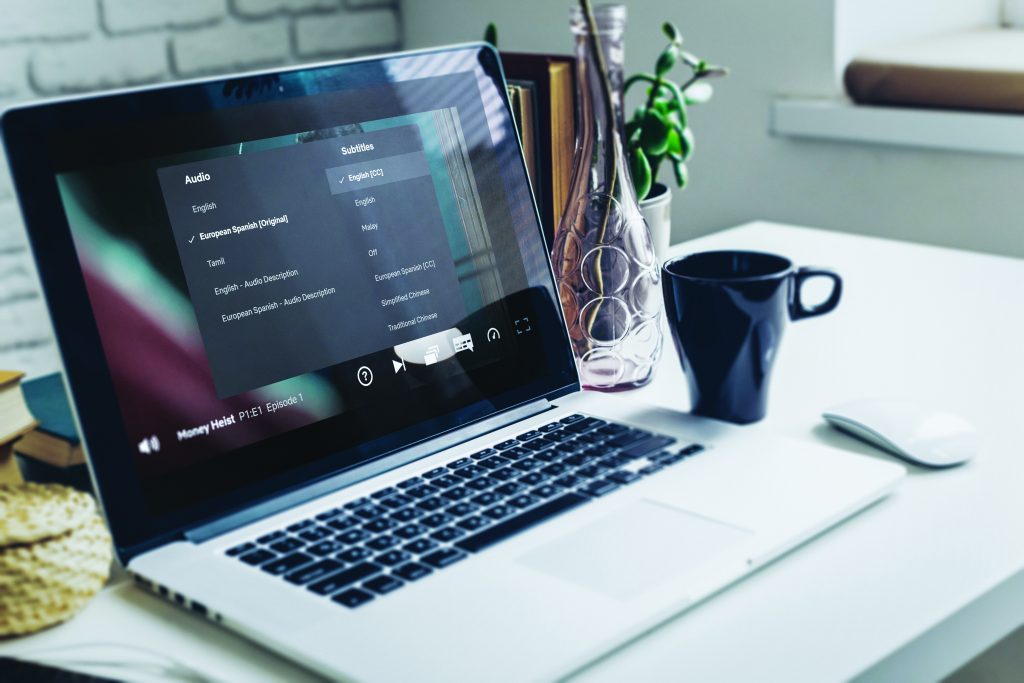

The streaming industry is seeing a major shift toward the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies, to minimise captioning and subtitling costs and maximise efficiency. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) and other ML technologies enable streaming providers to realise tremendous efficiencies in the media captions and subtitling workflow, including faster reviewing, reduced turnaround time, decreased manual efforts and lower costs.
ASR in particular allows video service providers to instantly recognise and translate spoken language into text, helping to streamline the creation of captions. It is now a powerful system that includes multiple components. With AI/ML, a one-stop solution can generate QC captions, subtitles and audio dubbing.
With AI- and ML-based QC solutions, video service providers can ensure that OTT content delivered to different geographies maintains outstanding quality. This is important, as today’s global audiences demand high-quality content, including captions. Moreover, with content going global, it is crucial to comply with strict regional and industry regulations. For instance, AI QC tools can ensure content meets the guidelines laid out by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the US. Advanced QC tools can also develop algorithms to check synchronisation between audio and subtitles in different languages.
Another key trend in video streaming is the increasing adoption of cloud technologies. The global video streaming software market is expected to more than double over the next few years, growing at a CAGR of 18.5% to reach $17.5bn in 2026, from $7.5bn in 2021. This shift to the cloud by OTT video service providers is apparent across the entire media workflow, from encoding to quality control (QC). Using a cloud-based ASR system, video service providers can reap all the benefits of the cloud to create captions and subtitles with increased flexibility, scalability and cost efficiencies.
Automated, AI-based improvements for dubbing workflows
Manual dubbing of audio is a complicated process that involves transcription, translation and speech generation. ML-based automated dubbing workflows exist, but their use is restricted for now. A common issue is a lead or delay between audio and video. Since the time it takes to communicate the same message in different languages varies dramatically, synchronisation problems may occur, with a negative effect on the viewing experience. Given how many streaming options are available today, service providers must deliver the best possible quality of experience, free of synchronisation issues.
“Using an AI-based automated QC solution, service providers can check synchronisation between dubbed track and master track with greater efficiency, to identify mismatches in the timing” – Manik Gupta, Associate Director of Engineering, Interra Systems
Automation is key to bringing greater efficiency to audio dubbing. Video service providers can for example verify complex dubbing packages, including multiple MXF and .wav files, ensuring that package variations are accurate and audio tracks are dubbed properly. Furthermore, automation can help video service providers confirm the precision of metadata package structures and check that the number of audio tracks, channel configuration of dubbed tracks and duration of the original audio track, compared with dubbed audio tracks, are correct.
Another key way in which the industry is tackling audio dubbing challenges is through innovations in automation and AI. Using an AI-based automated QC solution, service providers can check synchronisation between dubbed track and master track with greater efficiency, to identify mismatches in the timing. This is crucial to ensuring that there are no syncing issues.
Recent advances in AI have improved audio dubbing proficiency and quality, especially for language identification. AI/ ML algorithms have improved so much that automated QC systems can now detect language in any audio track with an accuracy of more than 90%. A key aspect is that training these models only takes a few hours; AI technology can then predict the dialect spoken in the audio track. Using metadata, content creators can then verify that this is correct.
It is thus anticipated that the streaming industry will increasingly rely on automated and AI/ML-based technologies to enhance audio dubbing efficiencies and improve the quality of content to a far greater level.
Conclusion
We know that video service providers are increasingly seeking to reach global audiences with the content they deliver, which means high-quality captions, subtitles and audio dubbing are now needed more than ever. The quality of streaming must be flawless in all respects.
Advancements in AI and ML technology are helping service providers extend the reach of their content to global audiences and capture additional viewers. Video service providers can now create and QC captions, subtitles and audio dubs with greater speed, accuracy and scale, without heavy investment in manual labour. AI and ML technologies ensure a high QE for global viewers on every device, cutting out the chance of human error.
In the future, streaming providers will need to embrace AI/ML- and cloud-based QC solutions as much as possible. Freeing humans from complex tasks such as transcription means they can focus on creative jobs such as translating difficult audio segments and adding audio descriptions. With an AI/ML solution, video service providers know that captions, subtitles and audio dubbing are of the quality and standard demanded by consumers today, keeping viewers satisfied no matter where they live and what device they’re watching on.
 Manik Gupta is Associate Director of Engineering at Interra Systems.
Manik Gupta is Associate Director of Engineering at Interra Systems.